Quick Start
Protein turnover, Proteomics, Mass spectrometry
Installing RIANA
Install Python 3.7+ and pip. See instructions on Python website for specific instructions for your operating system.
Riana can be installed from PyPI via pip or directly from GitHub. We recommend using a virtual environment.
$ pip install rianaLaunch riana as a module (Usage/Help):
$ python -m rianaAlternatively as a console entry point:
$ rianaTo test that the installation can load test data files in tests/data:
$ pip install tox
$ toxTo run the Riana test dataset (a single fraction bovine serum albumin file from a Q-Exactive) and write the results to a specified out/test/ directory
$ python -m riana integrate tests/data/sample1/ tests/data/sample1/percolator.target.psms.txt -q 0.1 -i 0,1,2,3,4,5 -o out/test/Processing Data
Project set up
RIANA requires the input mass spectrometry files to be in the mzML format. If you are not familiar with mzML files or received raw mass spectrometry files in vendor-specific formats (e.g., Thermo .raw), you can convert them to mzML using various tools, such as the msconvert tool from the ProteoWizard suite. Please refer to the ProteoWizard documentation for details.
Riana can be run either via Snakemake, or manually in command line.
Several of the intermediate files like the mzMLs can be quite large especially with modern instruments. Set up the file directory in a logical way and with enough storage. For instance, for a labeling experiment with multiple time points, you can set up the following directory structure:
├── /path/to/experiment/
│ ├── time0/
│ │ ├── fraction1.mzML
│ │ ├── fraction2.mzML
│ ├── time1/
│ │ ├── fraction1.mzML
│ │ ├── fraction2.mzML
│ ├── time3/
│ │ ├── fraction1.mzML
│ │ ├── fraction2.mzML
...Option 1: Running Comet, Percolator, and RIANA via Snakemake
RIANA comes with a Snakemake pipeline which is the recommended way to run RIANA. To configure, edit the provided config_template.yaml to specify the location of Comet and Percolator executables. Then run Snakemake with the provided Snakefile, e.g.,:
$ snakemake -c -s ./Snakefile -d out/snakemake_test --configfile ./config_template.yamlRefer to Snakemake documentations for details on configuring snake files.
Note that the provided Snakefile settings do not automatically output plotted curves or pre-integration intensity files by default. To output these files, edit the Snakefile to add -w and p to the shell commands under the integrate and fit rules, respectively.
Below is the config_template.yaml:
# Config
# Data location. Add as many lines as needed, sample names should be named after
# labeling time points (e.g., time12 for 12 days/12 hours of experiment)
data:
time0: /path/to/experiment/time0
time1: /path/to/experiment/time1
time3: /path/to/experiment/time3
time6:/path/to/experiment/time6
# Paths to the comet executable, the comet params file, the database, and the percolator executable
# The Snakefile assumes riana can be executed in the shell by riana
paths:
comet: /path/to/comet_source_2020013/comet.exe
comet_params: /path/to/params/comet.params
fasta: /path/tp/database.fas
percolator: /path/to/percolator
# Integration and fitting parameters
params:
model: simple # fitting model (simple, guan, fornasiero)
label_type: hw # labeling type (aa or hw or hw_cell)
isotopomers: 0,1,2,3,4,5 # isotopomer to integrate (0,1,2,3,4,5 for deuterium; 0,6 for heavy aa)
mass_tol: 15 # mass tolerance in ppm for integration (e.g., 25)
ria_max: 1 # final precursor ria
kp: 10 # guan model parameter (kp) or fornasiero model parameter (b)
kr: 0.15 # fornasiero model parameter (a)
rp: 5.52 # fornasiero model parameter (r)
depth: 1 # minimum number of data points
aa: K # which amino acid carries heavy label; only relevant if label_type is aa
mass_defect: D # which isotope mass defect to use (D, C13, SILAC)
fs: m0_mA # which mass isotopomer to use for heavy water labeling
# Number of threads
threads:
comet: 8
riana: 4
fitcurve: 12Option 2: Running RIANA manually
Alternatively, RIANA can be directly called from command line given the paths to the folder of the mzML files and the Search/Percolator results. To run the turnover analysis pipeline manually, prepare the following expected input files:
RIANA was tested on the percolator output file from Crux Tide/Percolator or standalone Comet/Percolator.
The following workflow has been tested for both amino acid and heavy water labeling data gathered on a Q-Exactive instrument:
Convert raw files to mzML, using
pwiz 3.0 msconvertin command line, with the following option:--filter "peakPicking vendor"
Download the latest Crux distribution
Run Tide index with the following options:
--digestion partial-digest--missed-cleavages
Run Tide search for each experimental time point separately with the following options:
--isotope-error 1,2(for HW) or6,12(for AA)--compute-sp T--mz-bin-width 0.02--mz-bin-offset 0.0--precursor-window 20--precursor-window-type ppm
Run Percolator with the following options:
--protein T--decoy-prefix DECOY_
Run RIANA
integratefor each experimental time point separately.Run RIANA
fit
Note that the mzml_path argument should point to the directory where all mzML fractions (fraction1.mzML, fraction2.mzML, etc.) for each labeling time point are located, whereas the id_path argument should point to a percolator.target.psms.txt file from the output of searching and post-processing all the mzML files in that labeling time point together
Output
RIANA integrate outputs a {sample}_riana.txt file for each sample, which contains the Percolator output appended with additional columns, e.g., m0, m6, m12, which contains the integrated areas of each isotopomer of each peptide over a retention time range in the mass spectrometry data. The output columns depend on the isotopomer indices specified.
In addition, the {sample}_riana_intensities.txt files contain the individual intensity data of each isotopomer in each retention time point prior to integration.
RIANA fit outputs a riana_fit_peptides.csv file which contains the best-fit k, R2, and dk for each peptide-charge combination.
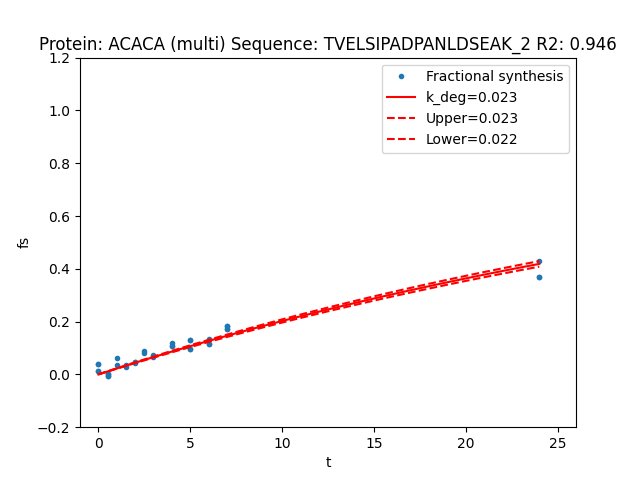
If the flag --plotcurves is set, RIANA additional outputs a graphical representation of each fitted curve: